
















Electrical stimulation uses 40–50Hz frequencies to trigger up to 20,000 deep contractions per session — building real strength while accelerating recovery.
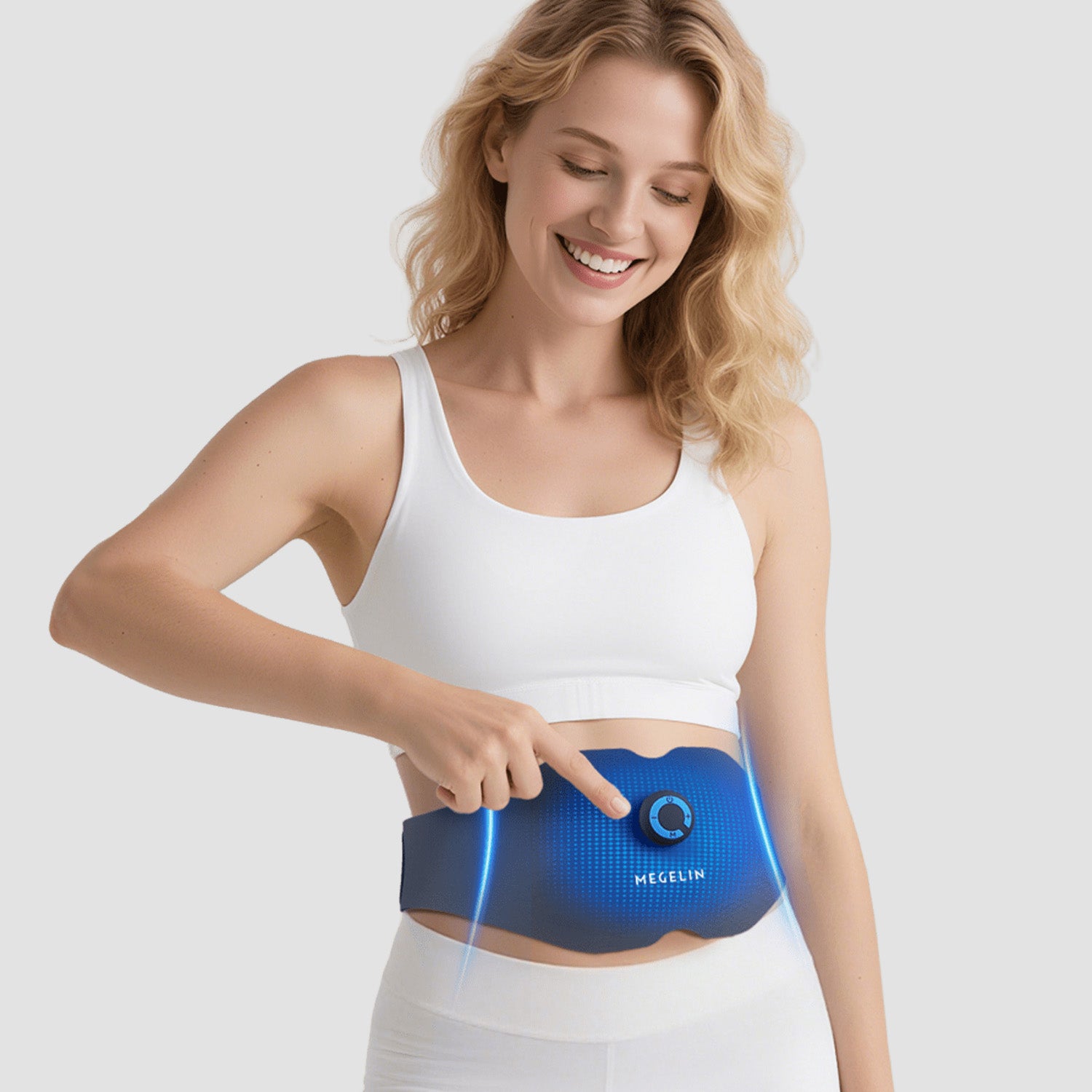
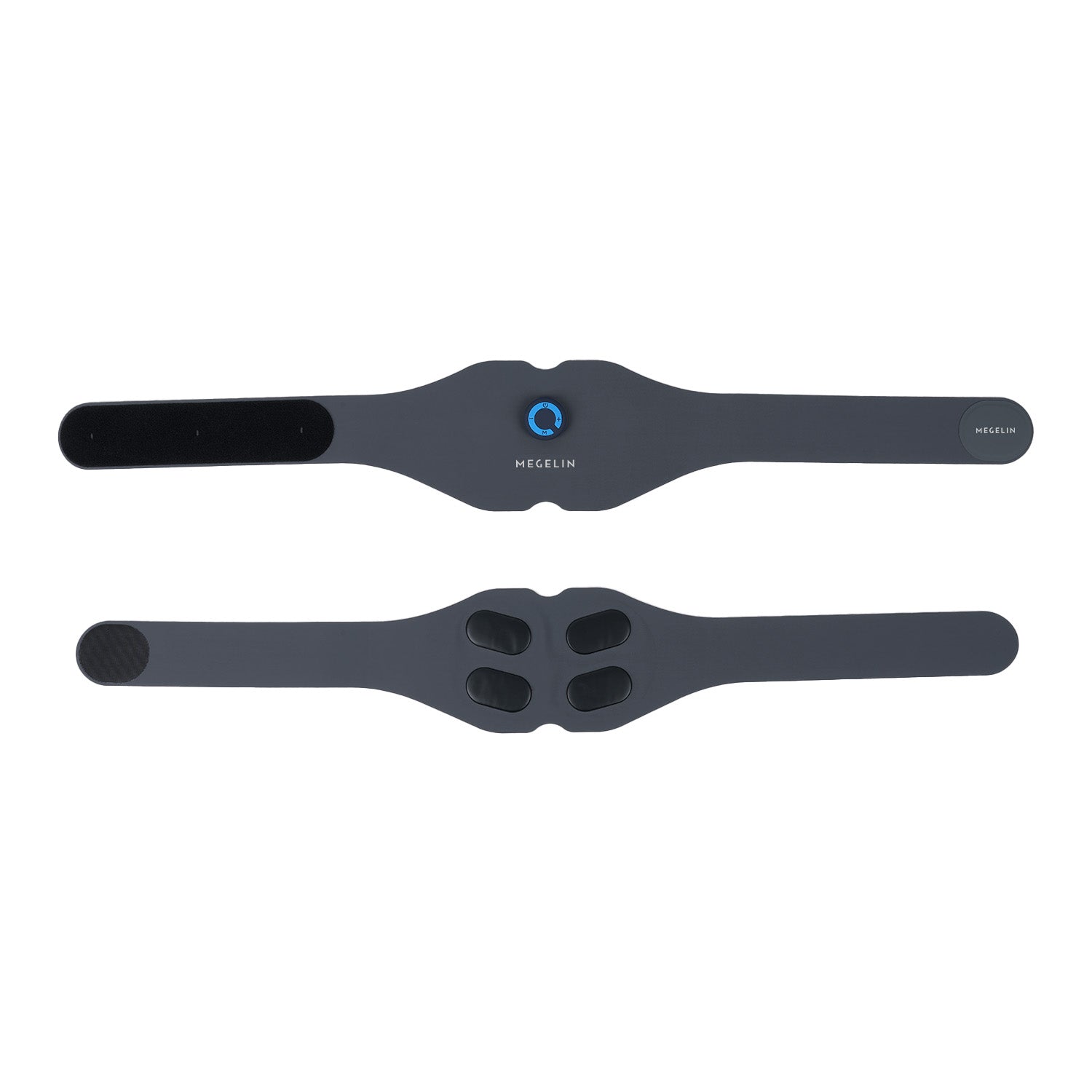
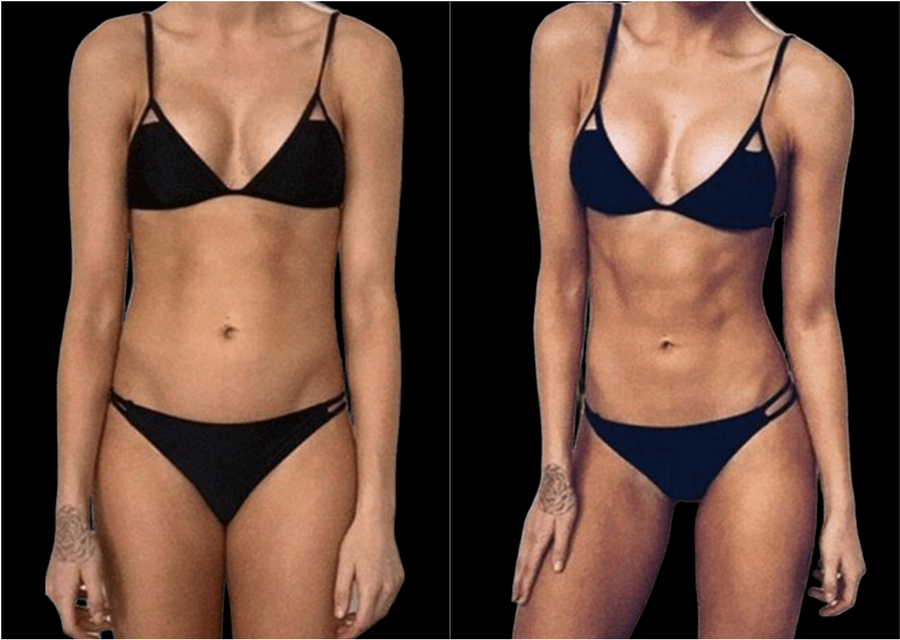
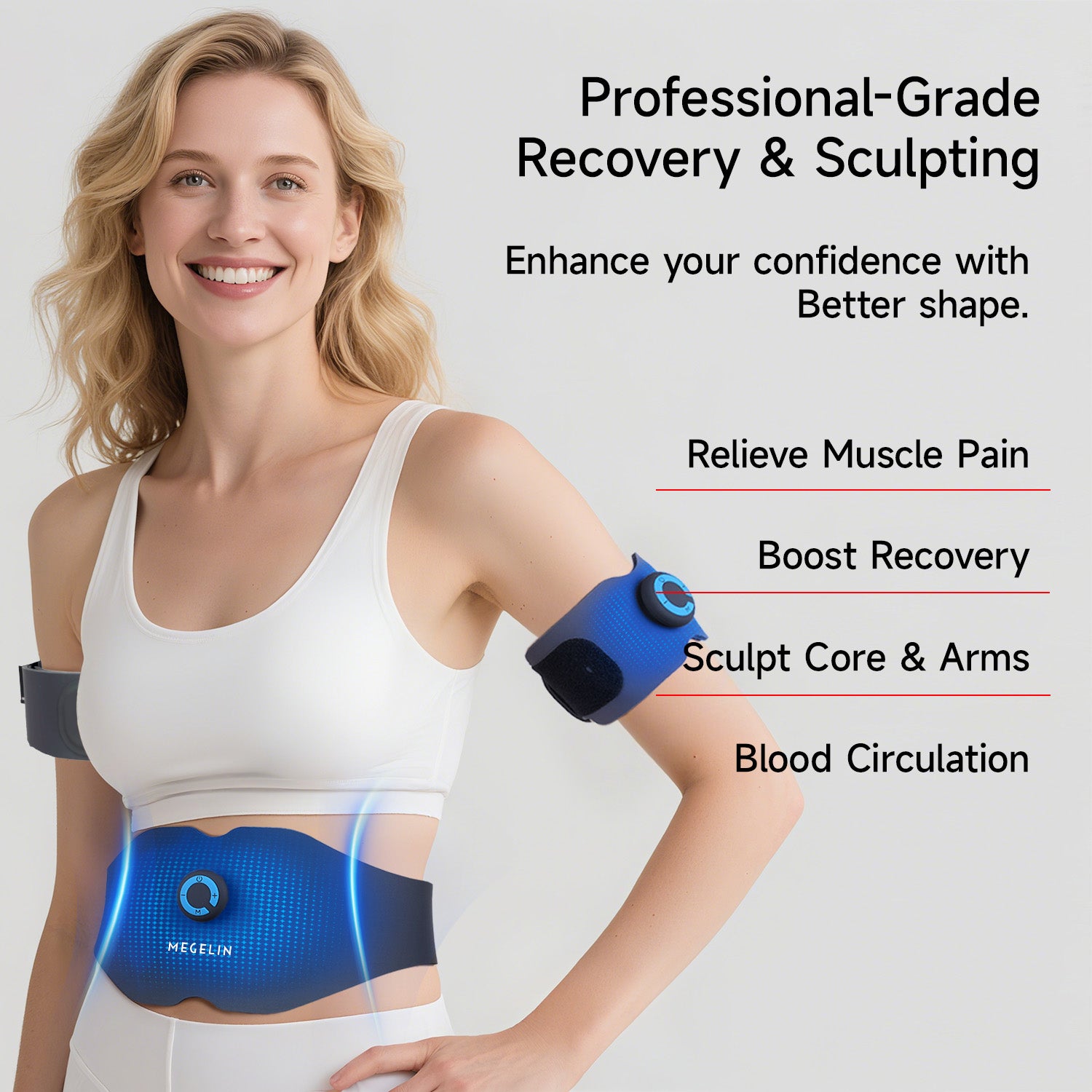
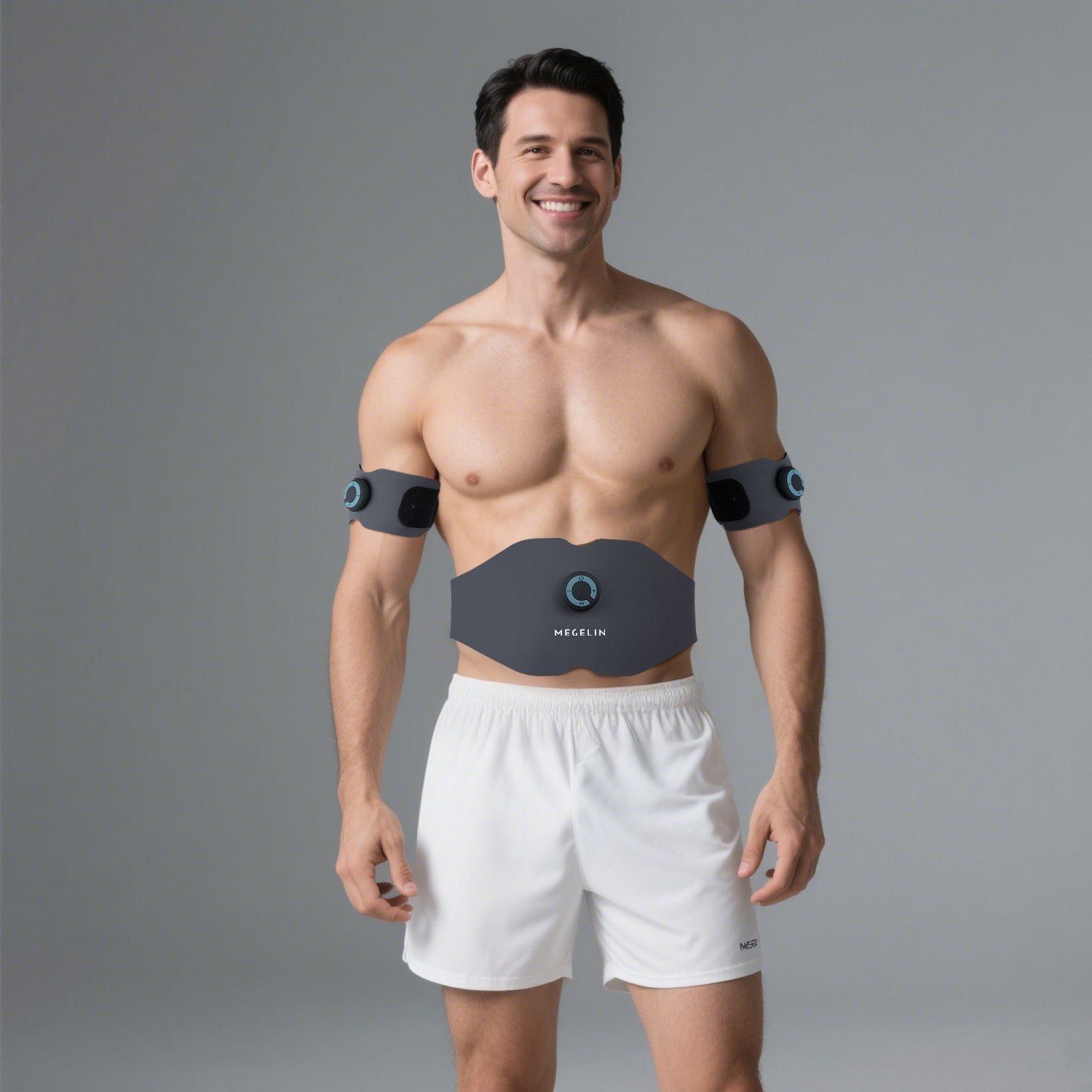
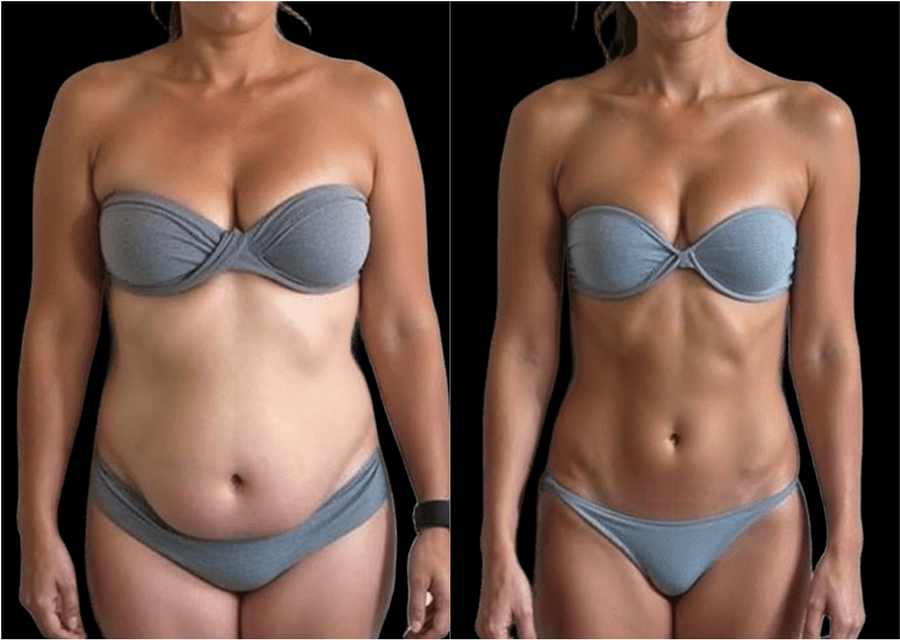
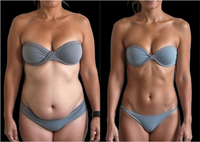
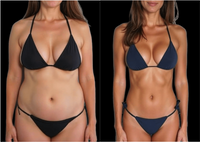
EMS pulses activate abdominal muscles for a firmer, more sculpted midsection. In 4–6 weeks, 94% of users reported stronger abs and improved definition.
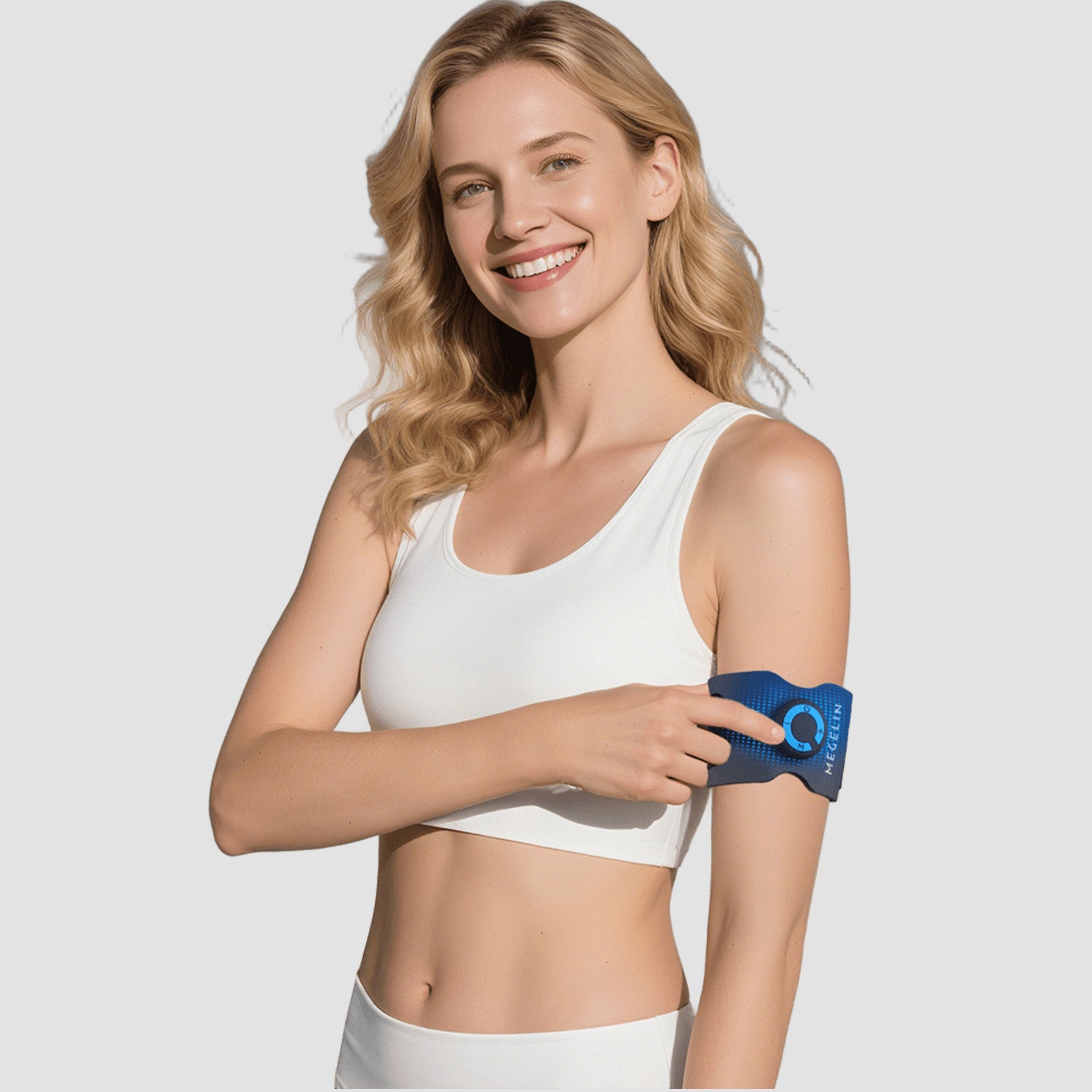
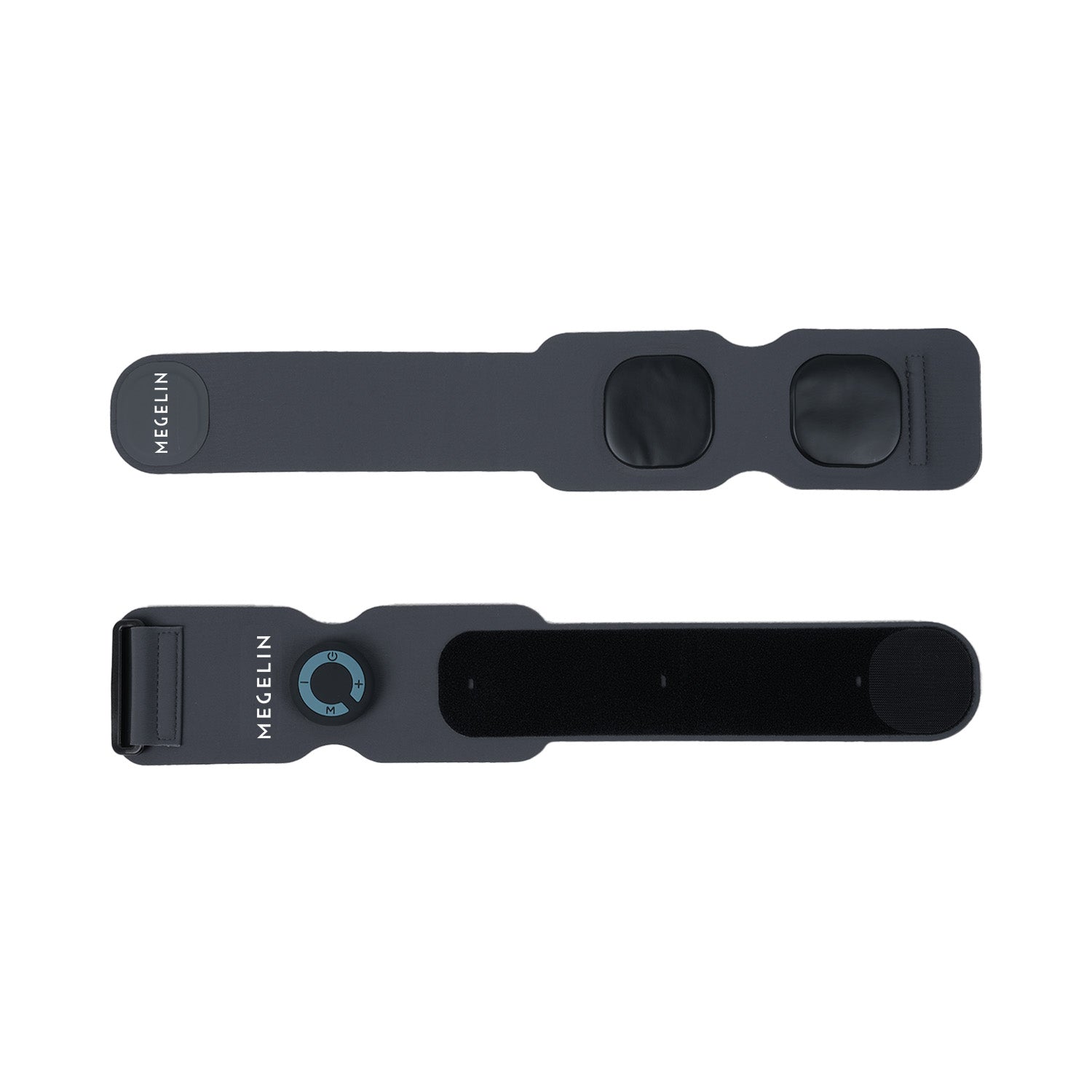
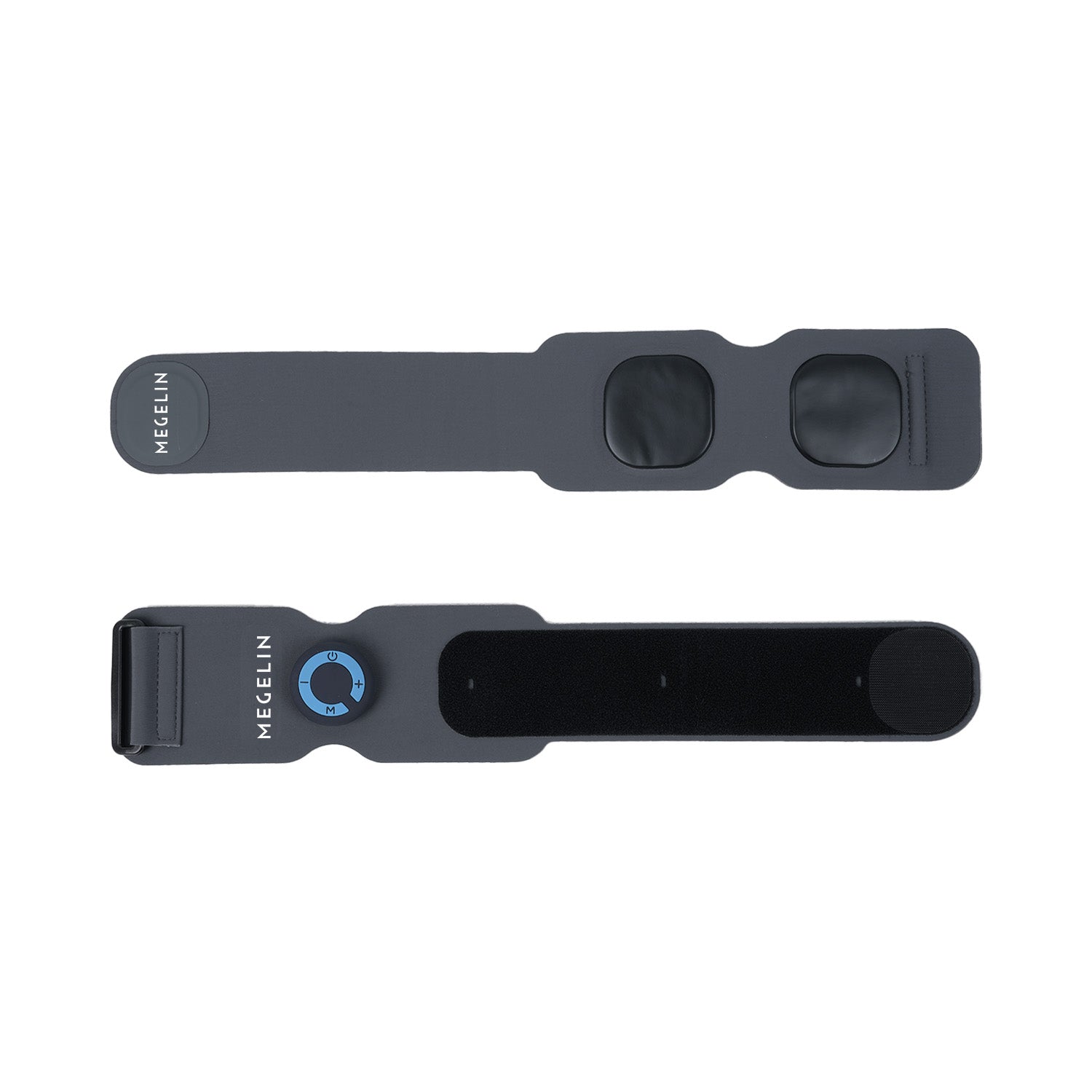
Targets upper and forearm muscles with supramaximal contractions. 92% of users noticed increased size and strength in just 3–5 weeks, with visible shaping and power gains.
Trusted Results, Real Users
Certified by SGS, the world's leading testing, inspection, and certification company.
EXPERIENCED
STRONGER ABS
EXPERIENCED
BIGGER ARMS
EXPERIENCED
SORENESS RELIEF


Science-Backed and FDA-Cleared
Over 4,000 NCBI-published studies validate EMS for muscle building, fat contouring, and recovery.

Backed By Thousands of Clinical Studies
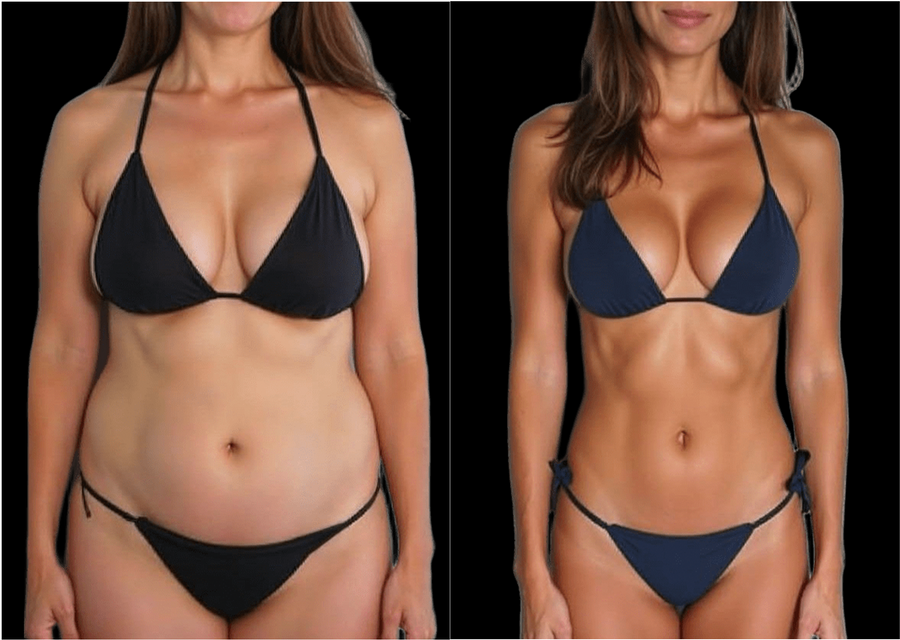
Over 4,000 NCBI-published studies confirm EMS is effective for muscle building, fat contouring, and recovery. It’s used in over 2.6 million rehab treatments annually, and has been clinically shown to activate deep muscle fibers more effectively than voluntary exercise.

FDA-Cleared for Contouring and Recovery
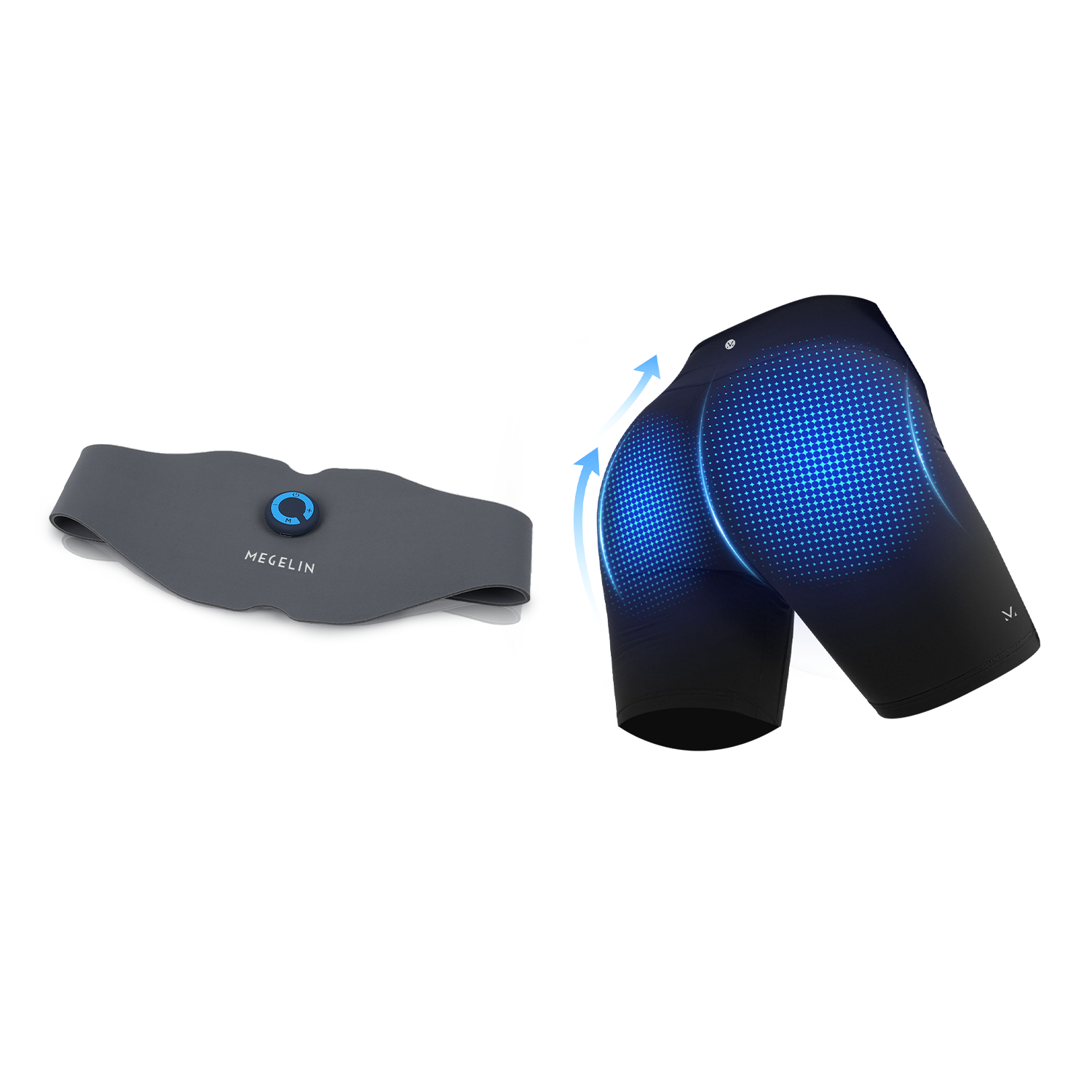
Megelin EMS Training System are FDA-cleared for the temporary relief of muscle pain and the enhancement of muscle performance.
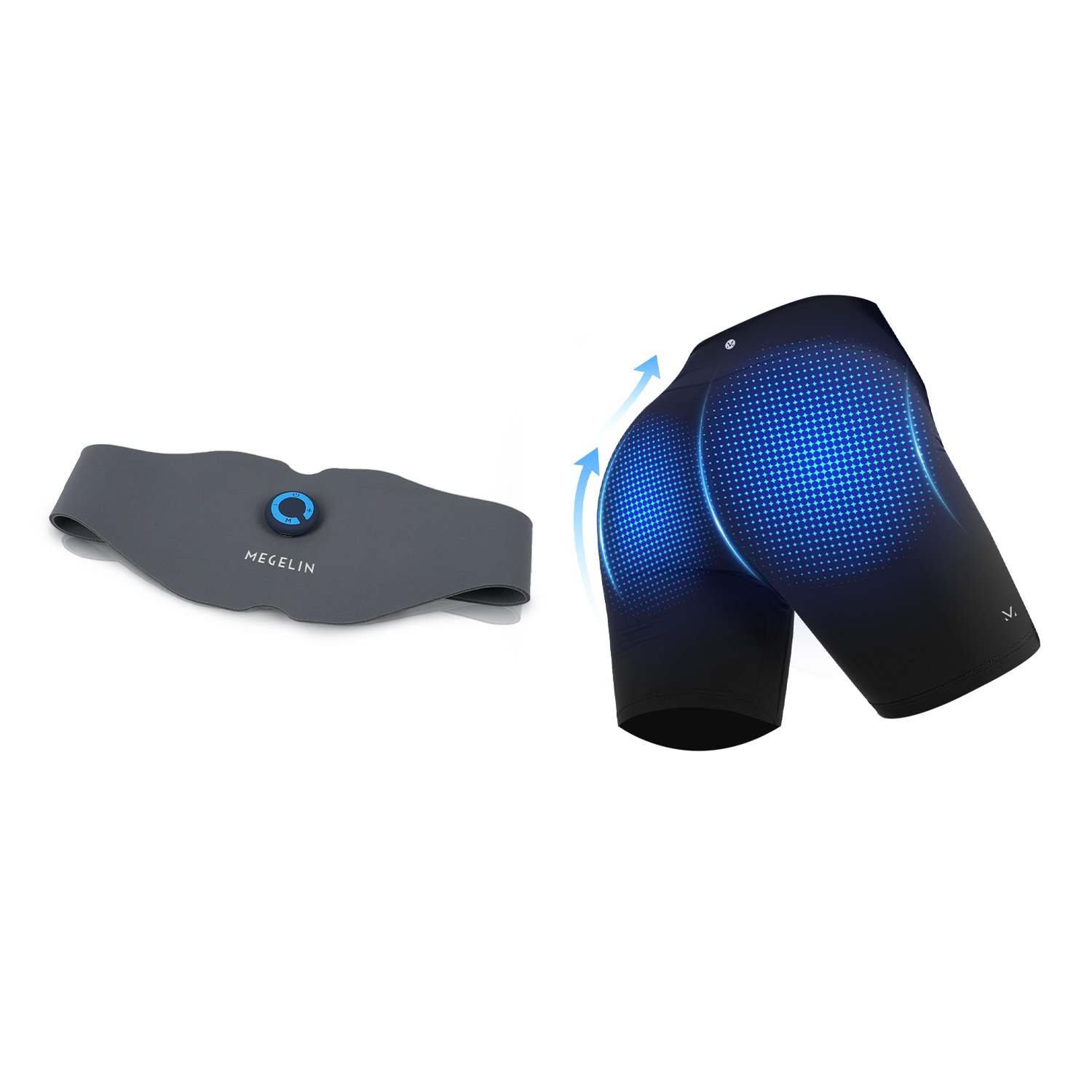
This makes it an effective tool for improving glute definition, supporting pelvic floor health, and strengthening the core.
Does EMS really help with muscle building?
Yes. The EMS Training System uses FDA-cleared electrical stimulation to trigger deep muscle contractions in the abs and arms — up to 20,000 per session. This mimics intense workouts, helping you build strength and definition over time.
How does EMS help with soreness relief?
Gentle stimulation improves blood flow and reduces lactic acid build-up, providing fast soreness relief within 15 minutes, especially after workouts or long sitting hours.
How long should each session last?
We recommend 15–20 minutes per session, 3–5 times per week, for best results.
Do I need to apply gel before use?
If your skin is naturally moist, no gel is required. However, during drier seasons—especially in winter—skin tends to be dry. For improved comfort and better conductivity, we recommend applying a conductive gel or lightly misting the skin with water before use.
Does it need to be plugged in?
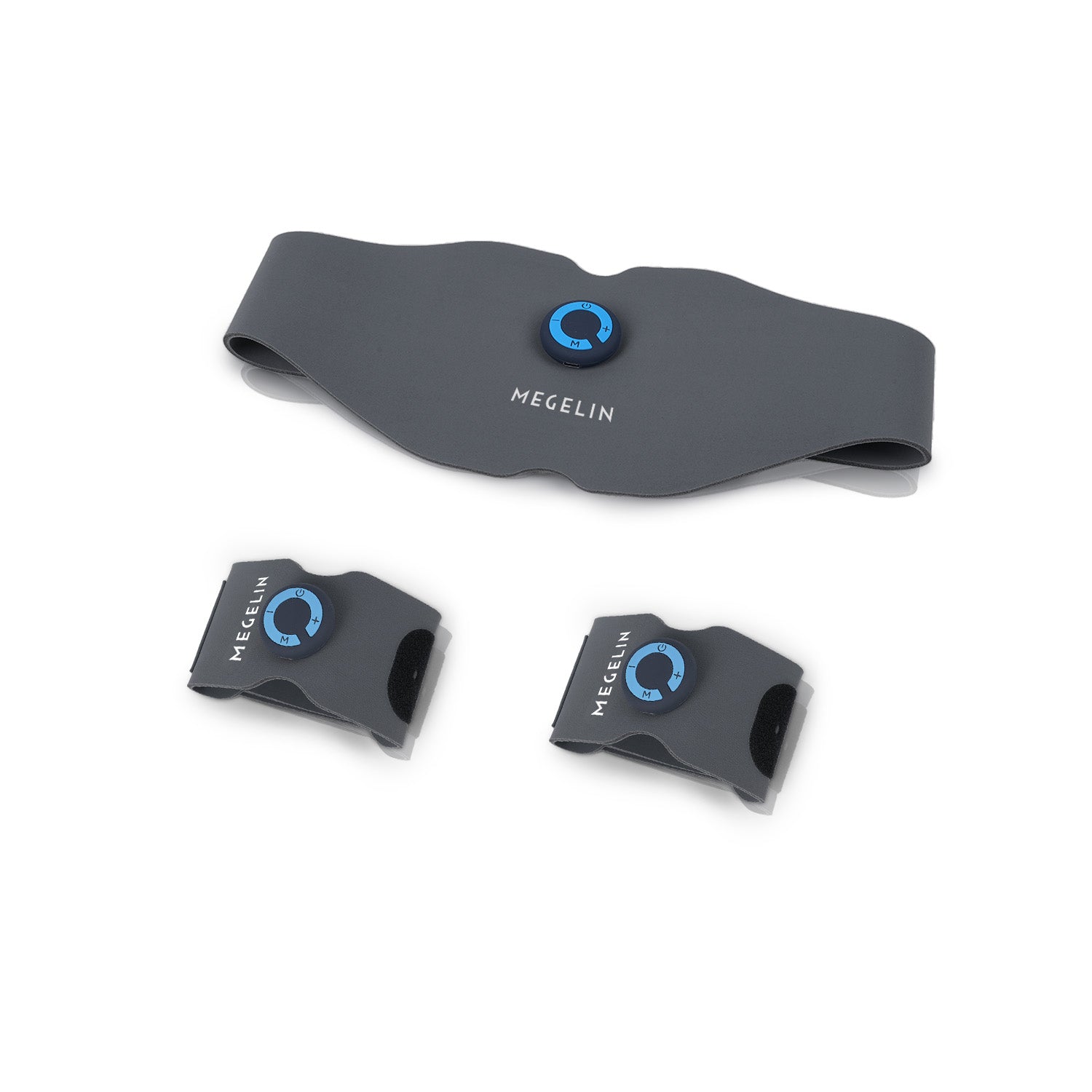
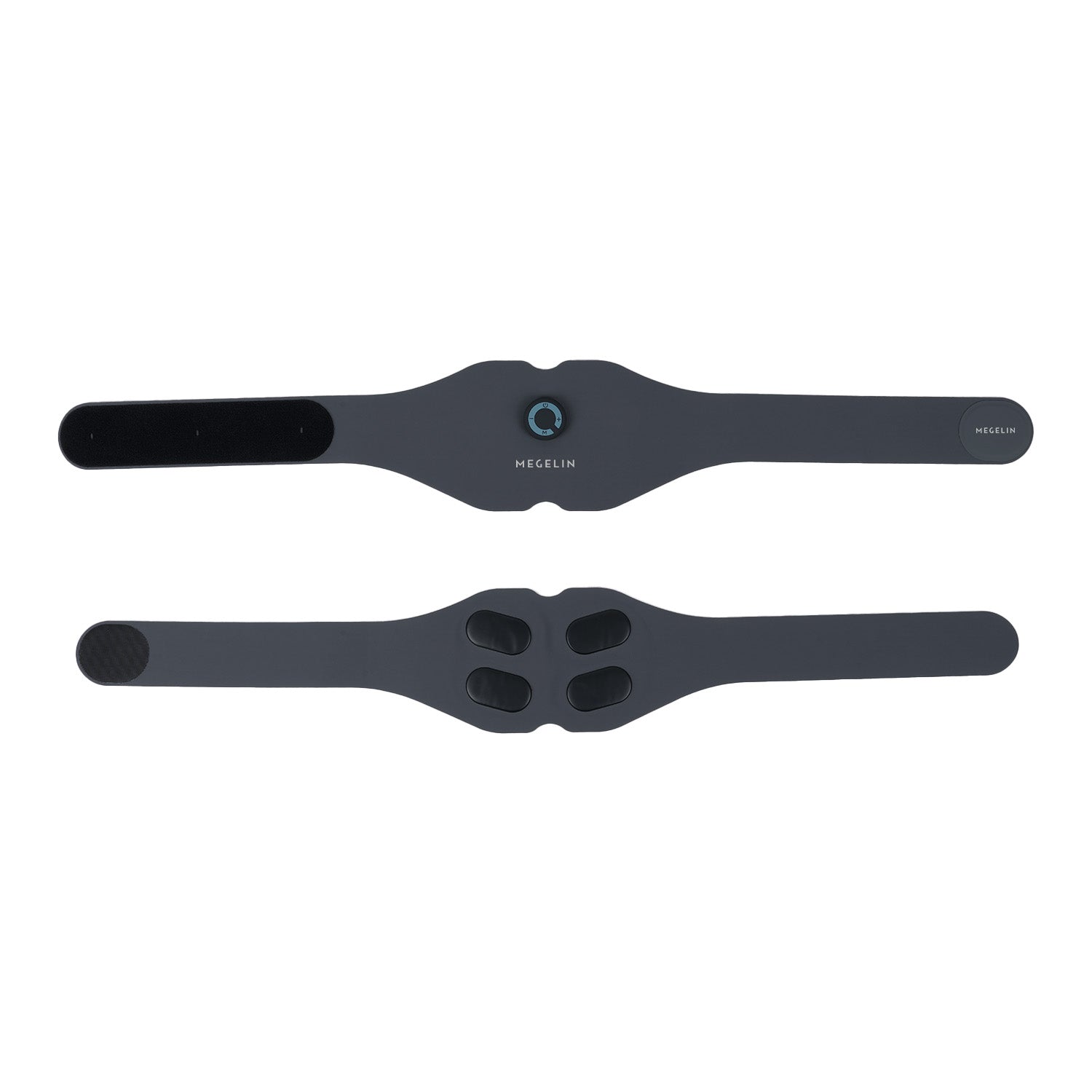
No. The EMS Training System is rechargeable and wireless, making it convenient to use at home, at work, or on the go.
































$279.00$279.00