Red Light Therapy and Vitamin D: Health Benefits and Tips
2MegelinIn an era where health and wellness are at the forefront of everyone's mind, the conversation around innovative therapies and essential vitamins is more pertinent than ever. Among the topics that have garnered significant attention, red light therapy and vitamin D stand out as pivotal elements in the pursuit of optimal health. Both have been shown to play crucial roles in various physiological processes, including but not limited to, enhancing mood, bolstering the immune system, and supporting bone health. However, understanding how red light therapy and vitamin D work together, and how one might influence the production and absorption of the other, opens up intriguing avenues for potential health benefits.
This article delves into the science and practical applications of red light therapy and vitamin D, outlining their individual benefits while exploring the synergy between them. From examining vitamin D sources and the mechanics behind vitamin D synthesis and delivery to the body's utilization of UV rays for vitamin D production, the narrative extends to how red light therapy supports cellular energy and vitamin D levels. Practical tips for incorporating red light therapy into one's routine for optimized vitamin D absorption will also be discussed. By the end of this exploration, readers will have a comprehensive understanding of how red light therapy and vitamin D can be harnessed to enhance their health and well-being, addressing common concerns such as vitamin D deficiency and the quest for more effective vitamin D supplements.
Understanding Vitamin D and Its Sources
Natural Sunlight
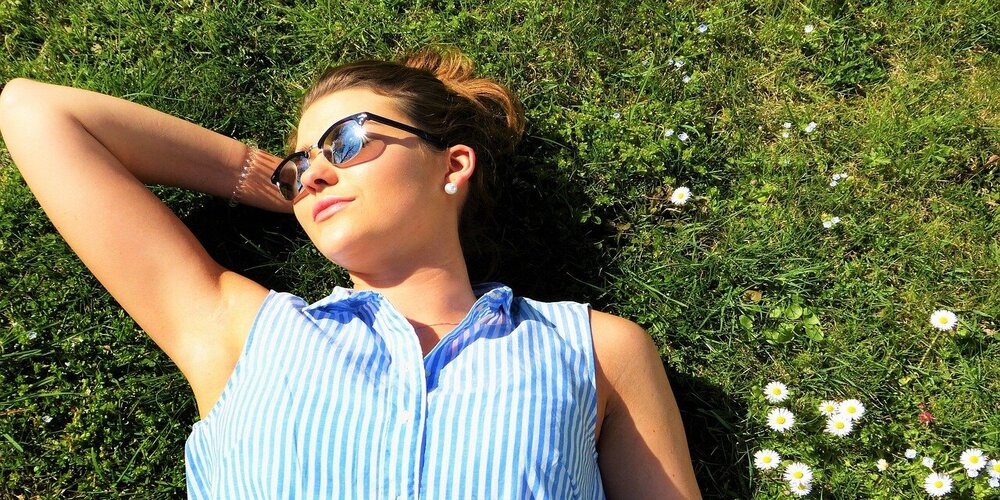
Vitamin D synthesis in human skin is initiated when it is exposed to UVB rays from natural sunlight. The optimal time for exposure is midday, particularly during summer when UVB rays are most intense. This allows individuals to produce sufficient vitamin D with minimal sun exposure [1][2]. However, factors such as geographic location, skin pigmentation, and the use of sunscreen can influence the effectiveness of sunlight in vitamin D production. For example, darker-skinned individuals and those living further from the equator may require longer exposure to sunlight to produce adequate levels of vitamin D [1][2].
Dietary Sources
While very few foods naturally contain significant levels of vitamin D, fatty fish like trout, salmon, and mackerel are among the best natural sources. Fish liver oils, particularly cod liver oil, are also rich in vitamin D, providing substantial amounts per serving [3][4]. For those who do not consume fish, mushrooms exposed to UV light can offer an alternative source of vitamin D [3]. Additionally, many countries fortify foods such as milk, cereals, and orange juice with vitamin D to help offset deficiencies [3][4].
Supplementation
Due to the limited availability of natural food sources rich in vitamin D and challenges associated with sufficient sun exposure, supplementation can be a practical approach to ensure adequate vitamin D intake. Supplements typically come in two forms: vitamin D2, derived from plants, and vitamin D3, which is the type produced in human skin upon sunlight exposure. Vitamin D3 supplements are often considered more effective at raising and maintaining adequate serum vitamin D levels compared to D2 [3]. It is essential to consider individual factors such as age, dietary preferences, and existing health conditions when choosing a supplementation strategy.
Red Light Therapy: How It Works and What It Does
Mechanism of Action
Red Light Therapy (RLT), also known as Photobiomodulation (PBM), utilizes low-level wavelengths of red and near-infrared light to stimulate cellular processes. The primary targets within cells are the mitochondria, often referred to as the "power plants" of the cells, where cytochrome c oxidase plays a crucial role [5]. Exposure to red light can lead to increased mitochondrial activity, which boosts production of adenosine triphosphate (ATP), enhancing cellular energy and efficiency. This process also results in a brief surge of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and nitric oxide, which are crucial for cellular signaling and vascular health [5].
Health Benefits
The therapeutic effects of red light therapy are extensive, ranging from enhanced skin rejuvenation and wound healing to inflammation reduction. By increasing collagen production, RLT helps in improving skin elasticity and reducing signs of aging such as wrinkles and fine lines [6][7]. It also aids in muscle recovery and joint health by reducing inflammation and pain [5]. For individuals with skin conditions like psoriasis or acne, RLT provides relief by decreasing inflammation and promoting healthier skin [7]. Additionally, it has been shown to improve healing rates in damaged tissues and organs [5].
Comparison with UV Light
Unlike UV light, which can cause skin damage and is associated with risks like skin cancer, red light therapy offers a safer alternative with no known adverse effects [8]. RLT operates at wavelengths that do not produce the harmful UV radiation, making it a non-invasive and low-risk option for daily use. While both sunlight and RLT are beneficial, they function differently; sunlight is essential for vitamin D production, whereas RLT focuses on enhancing cellular energy and health without the risks associated with UV exposure [8]. Combining moderate sunlight exposure for vitamin D synthesis with red light therapy for cellular health presents a balanced approach to harnessing light for improved wellness [8].
Practical Tips for Using Red Light Therapy
Choosing the Right Device
When selecting a red light therapy device, it's crucial to consider the specific needs it should address. Devices vary in terms of light wavelength, with options typically ranging from 600 to 900 nanometers. Those seeking skin benefits might prefer devices at 660 nanometers, while 850 nanometers could be better for deeper tissue and muscle recovery [9]. Additionally, the size of the device impacts its use; larger panels are suitable for broader areas like the torso, whereas smaller, more portable devices like wands or masks are ideal for targeted treatments [10].
Setting Up a Routine
To maximize the benefits of red light therapy, start with clean skin and position the device approximately 6 to 8 inches from the treatment area [11]. Initial sessions should last between 10 to 20 minutes and be conducted three to five times per week. After achieving desired results, maintenance treatments can be reduced to two to three times weekly [11]. It's essential to follow the specific guidelines provided with your device for the best outcomes.
Safety Considerations
While red light therapy is generally safe, proper eye protection is recommended, especially when using devices near the face [11][9]. This precaution is crucial for those with light sensitivity and helps prevent any potential discomfort. Furthermore, ensure the chosen device is FDA cleared to guarantee it meets safety standards, particularly when selecting a device for home use [12].
Conclusion
Throughout this comprehensive exploration, the dual significance of red light therapy and vitamin D in enhancing overall health has been clearly established, shedding light on their individual benefits and the synergistic effects of their combined application. By delving into the mechanisms behind vitamin D synthesis and the operational principles of red light therapy, this discussion has underscored their critical roles in boosting immune function, skin health, and cellular energy. The integration of practical tips for optimizing vitamin D absorption through sun exposure, dietary choices, and red light therapy application further empowers readers to make informed decisions in their health and wellness journey.
Reflecting on the insights shared, it's evident that the strategic use of red light therapy alongside ensuring adequate vitamin D levels can serve as a cornerstone in the pursuit of optimal health outcomes. The potential of these approaches to synergistically work hand in hand paves the way for innovative wellness strategies that go beyond conventional methods. As we continue to navigate the evolving landscape of health and wellness, embracing the implications of these findings and considering further research into their combined benefits could unlock new possibilities for enhancing well-being in our daily lives.
FAQs
Currently, there are no frequently asked questions available for "Red Light Therapy and Vitamin D: Health Benefits and Tips." Please check back later for updates or feel free to ask your own questions.
References
[1] - https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/vitamin-d-from-sun
[2] - https://www.solius.com/benefits-of-sunlight
[3] - https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/VitaminD-HealthProfessional/
[4] - https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/VitaminD-Consumer/
[5] - https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5523874/
[6] - https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/articles/22114-red-light-therapy
[7] - https://www.healthline.com/health/red-light-therapy
[8] - https://redlightman.com/blog/red-light-therapy-vs-sunlight/
[9] - https://www.health.com/best-red-light-therapy-devices-7759543
[10] - https://www.webmd.com/skin-problems-and-treatments/red-light-therapy
[11] - https://www.rehabmart.com/post/how-to-choose-a-red-light-therapy-device
[12] - https://www.verywellhealth.com/red-light-therapy-5217767