How Effective is Red Light Therapy for Vitiligo?
megelinbeautyVitiligo, an autoimmune disorder causing skin depigmentation, has long baffled dermatologists and patients due to its unpredictability. Among various treatment approaches, red light therapy stands out as a promising option. This treatment uses LEDs to stimulate skin cells, potentially improving pigmentation. With vitiligo becoming more common and a growing preference for non-invasive treatments, investigating red light therapy's effectiveness is crucial. This article will provide an overview of vitiligo, explore how red light therapy works, review scientific evidence on its effectiveness, and offer practical tips for incorporating it into daily routines. Finally, it will discuss the potential of red light therapy in managing vitiligo.
Vitiligo: Overview and Challenges
Definitions and Symptoms
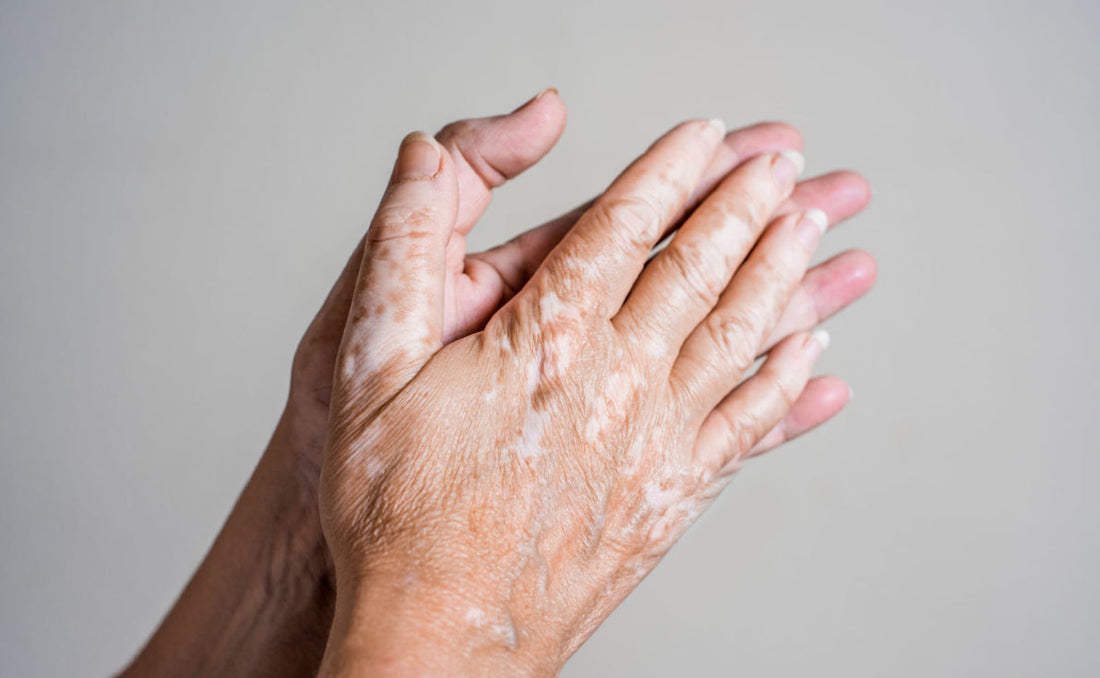
Vitiligo is characterized by the loss of skin color in distinct patches, a condition stemming from the malfunction or death of melanocytes, the cells responsible for producing melanin [1][2]. This depigmentation typically becomes more extensive over time and can affect any part of the body, including the skin, hair, and mucous membranes inside the mouth and nose. Notably, vitiligo can manifest in various forms, ranging from localized patches to nearly universal coverage [1]. The most common form, generalized vitiligo, shows symmetrical patchiness on corresponding body parts, while segmental vitiligo, less common, affects only one side or part of the body and usually ceases progression after a few months [2].
Psychological and Physical Impact
The impact of vitiligo extends beyond physical appearance, deeply affecting psychological and social well-being. Many individuals experience significant emotional distress, leading to issues such as anxiety, depression, and diminished self-confidence [3][4][5][6]. This distress can severely affect one's quality of life, influencing social interactions, employment opportunities, and even intimate relationships . The visibility of the patches, especially on visible areas like the face and hands, exacerbates these challenges, particularly in individuals with darker skin tones due to the stark contrast between affected and unaffected areas [7].
Furthermore, vitiligo is associated with other health risks, including an increased likelihood of sunburn and potential eye and hearing problems [1]. The chronic nature of vitiligo, coupled with its unpredictable progression, often necessitates continual management strategies, which may include cosmetic options like makeup or clothing to cover affected areas . In some cultures, the presence of vitiligo can also impact marital prospects and social standing, adding another layer of psychological burden .
In summary, while vitiligo is primarily visible as a skin condition, its ramifications are profoundly more extensive, touching on nearly every aspect of an individual's life. The management of vitiligo, therefore, requires a holistic approach that addresses both the physical and psychological components of the disorder.
Understanding Red Light Therapy
Technical Background
Red Light Therapy (RLT), a modality using low levels of red light, is engineered to improve cellular function by enhancing mitochondrial activity. The mitochondria, often described as the powerhouses of the cells, absorb this light, increasing energy production which, in turn, may accelerate cell repair and rejuvenation [8]. This form of therapy utilizes LEDs (light-emitting diodes) to deliver specific wavelengths of light, penetrating deeper into the skin compared to other light forms like blue LED, which is more surface-oriented [8].
The effectiveness of RLT hinges on its ability to stimulate collagen production, a critical protein for skin elasticity and health. It also boosts fibroblast production, which is essential for collagen synthesis, and enhances blood circulation to the tissues [9]. Importantly, RLT does not involve harmful UV rays, making it a safer alternative to traditional light therapies that might increase the risk of skin cancer [8].
Therapeutic Uses
Red Light Therapy has been explored for various medical and aesthetic applications. It shows potential in reducing inflammation, a common underlying factor in many chronic conditions, and has been used to manage pain related to conditions like rheumatoid arthritis and tendinopathy [8]. Its application extends to improving skin conditions such as wrinkles, scars, and signs of aging by promoting skin rejuvenation and increasing collagen levels [9][8].
Studies have documented the use of RLT in enhancing skin appearance, reducing symptoms of eczema, rosacea, and psoriasis, and even stimulating hair growth in conditions like androgenic alopecia [9]. Furthermore, it has been investigated for its effects on body contouring, where it may temporarily reduce body circumference through its action on adipose tissues [8].
The therapeutic scope of RLT also includes improving sleep quality, cognitive function, and overall well-being, making it a versatile tool in both clinical and home settings [10]. With ongoing research and clinical trials, the potential applications of Red Light Therapy continue to expand, offering hope for various conditions that are challenging to manage with conventional treatments.
Scientific Evidence Supporting Red Light Therapy for Vitiligo
Key Studies and Findings
Research into the efficacy of red light therapy (RLT) for vitiligo has shown promising results. A study utilizing 633 nm red light demonstrated an improvement in melanocytes' mitochondrial function, which is crucial for melanin production. This treatment led to marginal repigmentation in both skin and hair follicles by increasing adenosine triphosphate (ATP) production, thereby activating melanocyte regeneration [11]. Furthermore, consistent daily treatments with red light have been highlighted as crucial for maintaining melanocyte health and proliferation, suggesting that regularity in treatment may enhance the repigmentation process [11].
Comparative Analysis with Other Light Therapies
Red light therapy's effectiveness can be juxtaposed with other established light therapies like Psoralen plus Ultraviolet A (PUVA) and narrowband ultraviolet B (NB-UVB). Studies have indicated that patients undergoing NB-UVB treatment often experience higher rates of repigmentation compared to those receiving PUVA [12]. Moreover, excimer laser phototherapy, another form of targeted light therapy, has shown significant improvements in repigmentation over shorter treatment durations compared to standard therapies [12]. These findings suggest that while traditional light therapies remain beneficial, RLT and other targeted phototherapies may offer more efficient repigmentation results.
Mechanisms Involved in Treatment
The therapeutic potential of RLT in vitiligo treatment is largely attributed to its ability to enhance mitochondrial function and reduce inflammation, which are critical in autoimmune conditions like vitiligo [11][13]. By increasing ATP production, RLT aids in the revitalization and repair of cells, which is fundamental for the regeneration of healthy skin cells, including melanocytes [13]. Additionally, the anti-inflammatory properties of RLT may alleviate autoimmune damage to skin cells, thus preventing abnormal function and early melanocyte death, which are pivotal in achieving successful repigmentation [13].
In conclusion, the scientific evidence supporting the use of red light therapy in vitiligo treatment is compelling, with studies highlighting its ability to improve mitochondrial function, enhance cell regeneration, and offer a safer alternative to traditional light therapies. The ongoing research and clinical trials continue to underscore the potential of RLT as an effective treatment modality in managing and potentially reversing the effects of vitiligo.
Implementing Red Light Therapy in Daily Life
Practical Tips
Implementing red light therapy (RLT) into daily life requires an understanding of the device setup and the environment in which it will be used. Individuals should select FDA-approved RLT devices that specify wavelengths suitable for treating vitiligo. It's essential to create a comfortable area for therapy sessions, ideally a quiet, private space where the light can be directed accurately to affected areas.
Frequency and Duration of Treatment
The frequency and duration of red light therapy sessions can significantly influence the effectiveness of the treatment for vitiligo. Initial guidelines recommend starting with shorter sessions, approximately 15-20 minutes, conducted three to four times a week. Observing the skin's response over a few weeks is crucial; if positive changes are noted, the duration can be gradually increased to daily sessions, ensuring not to exceed 30 minutes per session to prevent skin irritation.
Monitoring Progress and Adjustments
Regular monitoring of the skin's response to red light therapy is essential for adjusting treatment parameters effectively. Individuals should document the progress of repigmentation through weekly photographs of the affected areas. These images provide a visual reference to assess the effectiveness of the treatment over time and help in determining if adjustments in frequency or duration are needed. If progress plateaus or if any adverse reactions occur, consulting a dermatologist is advised to tailor the therapy to individual needs and ensure safety.
Conclusion
Through the exploration of red light therapy (RLT) in the treatment of vitiligo, it becomes evident that this innovative approach holds substantial promise for individuals grappling with this challenging condition. The article has illuminated the scientific underpinnings of RLT, from its effectiveness in enhancing mitochondrial function and promoting melanogenesis to its comparative advantages over traditional light therapies. Embedded within these discussions is a broader narrative on the need for safe, effective, and non-invasive treatment options for vitiligo, underscoring the potential of RLT to meet these criteria and improve patients' quality of life.
As we navigate the complexities of managing vitiligo, the convergence of scientific evidence and practical guidance on implementing RLT presents a beacon of hope for many. The significance of this treatment modality extends beyond the physical repigmentation of the skin; it encompasses the restoration of confidence, social well-being, and overall life satisfaction for those affected. Recognizing the imperative for further research to solidify RLT's position within vitiligo treatment regimes, the article encourages ongoing inquiry and clinical experimentation. Embraced with an informed perspective, individuals with vitiligo and their healthcare providers can consider red light therapy as a potentially transformative tool in their therapeutic arsenal.
FAQs
1. How effective is red light therapy in treating vitiligo?
Red light therapy, using He–Ne lasers, and blue light therapy, using LEDs, can both stimulate the repigmentation of skin in vitiligo patients with minimal side effects. Additionally, Q-switched ruby and FD Nd:YAG lasers are effective depigmentation treatments that can be used alone or in conjunction with topical agents.
2. What is the success rate of phototherapy in treating vitiligo?
A meta-analysis of 35 studies, which included 1428 patients, showed that narrowband UV-B phototherapy led to at least a mild response in 74% of patients at 6 months and 75% at 12 months. A marked improvement was observed in 19% of patients at 6 months and 36% at 12 months.
3. What is currently the most effective treatment for vitiligo globally?
Ruxolitinib (Opzelura™) is the only treatment approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for restoring lost skin color in individuals with vitiligo. This JAK inhibitor cream is suitable for treating people aged 12 and older with non-segmental vitiligo.
4. Is there a possibility of vitiligo returning after phototherapy treatment?
Studies have shown that the face and neck areas have a high rate of both cure (73.7%) and relapse (88.5%) following treatment. Continuous treatment with methods such as topical corticosteroids, calcineurin inhibitors, and UVB phototherapy is crucial to prevent new outbreaks after successful repigmentation.
References
[1] - https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/vitiligo/symptoms-causes/syc-20355912
[2] - https://www.niams.nih.gov/health-topics/vitiligo
[3] - https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC10566310/
[4] - https://www.dermatologytimes.com/view/the-psychosocial-impact-of-vitiligo
[5] - https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6607222/
[6] - https://kdcclinic.com/blogs/phototherapy-in-vitiligo-treatment/
[7] - https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC10636619/
[8] - https://www.webmd.com/skin-problems-and-treatments/red-light-therapy
[9] - https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/articles/22114-red-light-therapy
[10] - https://platinumtherapylights.com/blogs/news/the-history-of-red-light-therapy
[11] - https://platinumtherapylights.com/blogs/news/red-light-therapy-for-vitiligo
[12] - https://www.bcbsm.com/amslibs/content/dam/public/mpr/mprsearch/pdf/2043115.pdf
[13] - https://rouge.care/blogs/rouge-red-light-therapy-blog/harnessing-the-power-of-red-light-therapy-for-vitiligo